Search engines help users find the most relevant and useful results to their search queries. To do this, they index and rank websites based on various factors, including the quality and uniqueness of the content. When search engines encounter duplicate content on the same or different domains, it can create many problems.
First, it can make it difficult for search engines to determine which version of the content is more relevant. This can lead to lower rankings for all versions of the content. That happens even if some of them are actually more relevant than others. Additionally, duplicate content dilutes the overall quality of a website’s content, leading to lower rankings.
What does duplicate content mean?
Duplicate content generally refers to textual content that appears on the Internet in more than one place. There are two types of duplicate content — internal and external:
- Internal duplicate content occurs when the same content appears on more than one page of a website. This can happen for many reasons including accidentally duplicating content on the same domain when creating new page. It can also happen if deliberately duplicating content to manipulate search engine rankings.
External duplicate content is when the same content appears on more than one website. This can happen when two websites scrape content from each other. It can also happen when a website syndicates its content to other sites.

Why do duplicate content issues appear & How to fix them?
Duplicate content issues arise when the same content appears on multiple web pages. This can happen for several reasons.
Boilerplate content
Duplicate content on the same domain occurs when you have identical or very similar content on multiple site pages. This can happen when you have boilerplate content that appears on every page (e.g., your site’s navigation or footer). It can also happen if multiple pages with very similar content.
- Be unique and relevant content for every page. Avoid using boilerplate content or content exactly the same on multiple pages. Blog posts and commercial pages should be unique to rank high in search engines. This means that content is fresh and not duplicated from sources.
E-commerce product pages can often be quite similar, especially if the products are from the same manufacturer. However, unique content is required for your articles to rank on Google. This unique content can be product descriptions, customer reviews, or even blog posts related to the product.
- Unique page title, H1, and meta description in the HTML code for each page help search engines understand what each page is about. From there, they can determine which pages to show in the search results. Your page title and H1 tag should be concise, keyword-rich, and accurately reflect the content of your page. In addition, your meta description should be a brief, keyword-rich description of your page. The goal is to encourage clicks from organic search results.
Creating unique, keyword-rich titles, H1 tags, and meta descriptions for each page on your website are vital for on-page SEO. By doing so, search engines will properly index your pages. Finally, your organic search results are more likely to get clicked.
Same content on different URLs
Faceted/filtered navigation organizes content so that users can narrow down their options by selecting different criteria. This can cause duplicate content because the same content may be accessible via multiple URLs with varying combinations of filters applied.
For example, if a user filters a list of products by price and the resulting list is identical to the previous one, it is considered duplicate content.
For a seamless way to identify and manage canonical issues, the Attrock Canonical Tag Checker is an great tool for optimizing your website’s SEO performance.
The rel=canonical attribute goes in the <head> section of your HTML code, and looks like this: <link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.example.com/original-page.html” /
In this example, the rel=canonical attribute tells search engines that the page at http://www.example.com/original-page.html is the original version of the content. Any other pages on the website with identical content should use the rel=canonical attribute to point to the original page.

Content scraping
Scraped content is content that has been copied from another source without permission. It is often of lower quality than original content and can be considered plagiarism. If you’re concerned that someone may have copied and pasted your content without permission, there’s a simple way to check using Google Search. Just enter a few phrases from your content into quotation marks and see if anyone else on the web has used those exact phrases.

The other and more straightforward way is to use plagiarism checkers. It’s a tool where you can paste the text or URL and compare the content with the existing database.
1 – Contact the website.
If you come across your content on another website that you did not permit to post, you can reach out to the website and request to remove it. When writing an email, be sure to include the URL of the page where your content appear. You should also add a brief explanation of why you are requesting that it be removed.
2 – Ask to use the canonical link.
When you reach out and request to add a canonical link to your site’s original page, you ask them to help you with your search engine optimization (SEO) efforts. Having a canonical link on their site will increase your chances of being found when people are searching for your content. In addition, it will help to improve your search engine rankings, as search engines will see that your content is being linked from other websites.
3 – Send a request to Google.
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act, a U.S. law that provides certain protections for online service providers against copyright infringement, can also help with scraped content. If you believe that someone has posted your copyrighted material on an online service provider without your permission, you can file a request for removal under the DMCA. Thus, sending a request to Google will help you get particular duplicate content removed from Google’s services.
4 – Do not scrape content.
In eCommerce, marketers often take all the content from the manufacturer and use it as is. This can be a good thing, ensuring that customers get accurate and up-to-date information. However, it can also be a bad thing, leading to duplicate content. Try to avoid copying content already published and indexed online, as it’s considered content scraping. This can be damaging to both the original content creator and your own site, as it can result in decreased traffic and search engine penalties.
Technical tips for dealing with duplicate content
1. Examine all content and tags
When you’re improving your website’s SEO, an important task is to ensure that there’s no duplicate content on the same domain. This means examining all of your site’s content, including pages and blog posts and any tags or other metadata. If you find any duplicate content, you’ll need to either remove it or canonicalize it so that search engines can easily identify the source.
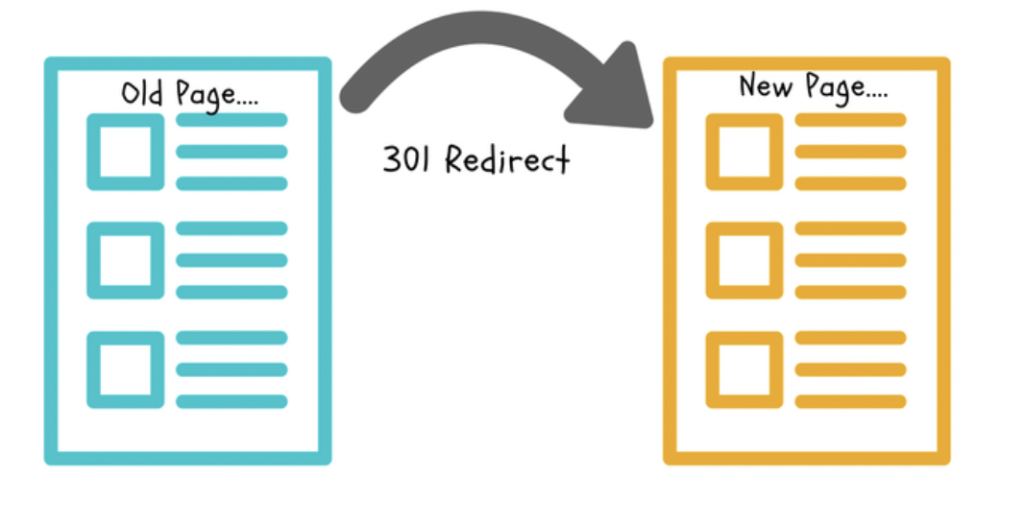
2. Set up 301 redirects from the “duplicate” page to the original content page
A 301 redirect is an HTTP status code that tells a web browser that a page has been permanently moved to a new location. When a browser sees a 301 redirect, it automatically goes to the new page. Suppose you have a page on your website that is very similar to another page. In that case, you can set up a 301 redirect so that visitors will be automatically redirected to the original page.
3. Use the content=”noindex, follow” robots meta tag to exclude the page from a search engine’s index
When you use the content=”noindex, follow” robots meta tag, you tell the search engine not to index the page but follow any links on the page. This is useful if you have a page that you don’t want people to find through the search engine, but you still want the search engine to follow the links on the page.
4. Keep your internal linking consistent
If you’re linking to your own content, be compatible with how you format your links. That means using the same anchor text and link URL for each link throughout your website. This will help keep your site organized and easy to navigate, and it will also help search engines crawl and index your content more effectively.
5. Be careful about other tech errors
A few other technical errors lead to duplicate content that the SE Ranking’s site audit can automatically spot.
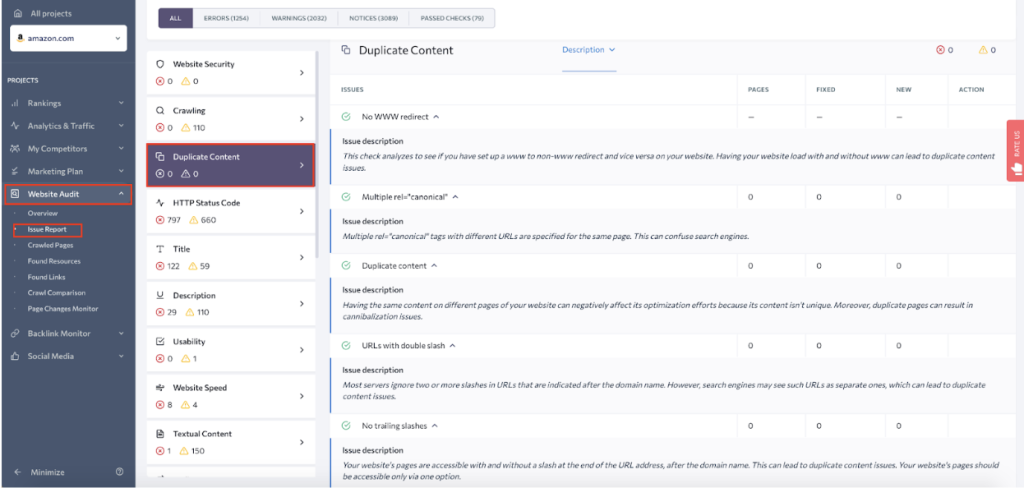
One common error is using different URLs for the same page. This can happen if a website has both www and non-www versions or HTTP and HTTPS versions are not properly redirected. Another error is using different parameters that might lead to duplication, such as website mirrors.
A website mirror is a complete copy of a website hosted on a different server. It can cause problems if not configured correctly. One common problem is duplicate content, which can occur when search engines index the same content on both the original website and the mirror. To avoid these problems, it is important to configure website mirrors correctly and to ensure that only unique content is served on each mirror. You can also use the rel=”canonical” tag to specify the source of the content, which will help search engines index and rank your content correctly.
6. Make sure syndicated content is on the appropriate site
When syndicating content, it is crucial to ensure that the sites on which the content is published are legitimate. This means that the sites should have a good reputation. Additionally, the sites should be appropriate for the content being published. For example, if the content is related to finance, it should be posted on a site known for providing accurate and reliable information about finance.

How does duplicate content impact SEO?
Duplicate content is a common issue on the internet, and it can have a significant impact on your website’s SEO. Let’s have a deeper look at it:
Poor rankings
When it comes to SEO, quality is always better than quantity. This is especially true when it comes to content. Duplicate content is considered to be low-quality by search engines and will not rank as high as original, well-written content. Search engines want to provide users with the best possible results, and duplicated content isn’t as good as unique content.
Less organic traffic
There are a few reasons why having duplicate content on your website can lead to less organic traffic. First, if there are multiple pages with the same content, search engines may have a hard time determining which page is most relevant to a given search query. As a result, your pages may be ranked lower in search results, and potential visitors will never get to your content. Additionally, if people find your duplicate content, they may be less likely to engage with it since they’ll feel like they’ve already seen it before. This can lead to less overall organic traffic, as well as less engagement and conversions.
Penalty or complete deindexing of a website
Duplicate content is a major issue for SEOs and can cause a website to be penalized or even deindexed by Google. To avoid being penalized, it’s important to make sure that all of your website’s content is unique. One way to do this is to use a tool like Paraphraser to check plagiarism. If you find duplicate content on your site, you’ll need to either remove it or rewrite it so that it’s unique.
Conclusion
There’s no denying that duplicate content can be a big problem for any website. After all, if you have multiple pages with identical or similar content, it can be difficult for search engines to figure out which page is the most relevant. It hurts your search engine rankings and leads to a decrease in traffic and conversions. The good news is that you can identify and fix duplicate content issues on your site by taking the steps mentioned above.
Moreover, duplicate content isn’t always a bad thing. In some cases, when you just have a handful of duplicate content, it won’t lead to penalties from Google. So while it’s essential to be aware of the potential problems that duplicate content can cause, it’s not always something you need to worry about.

